At its second annual "The Check Up" event on Thursday, Google shared its research on new health projects that aim to use smartphones to protect cardiovascular health, preserve eyesight, and record heart sound.
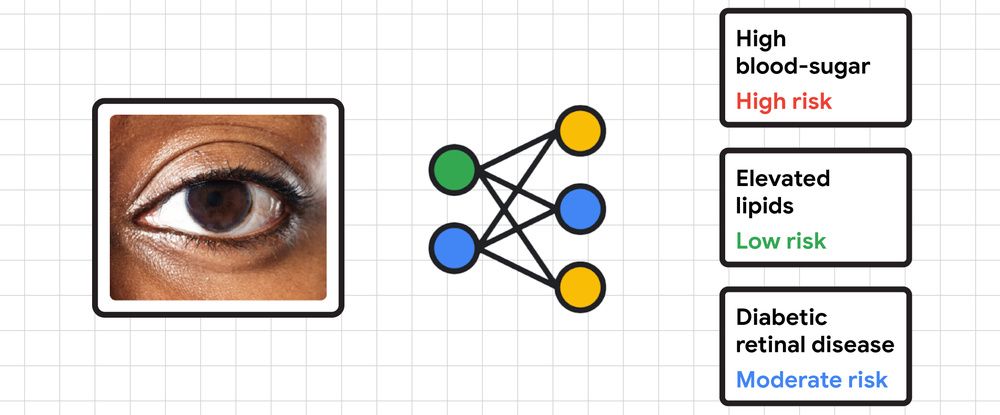
The first project builds upon Google's previous research, which tackled detecting cardiovascular risk factors such as high blood sugar and cholesterol levels and diabetic eye disease using clinical photos of the interior of the eye. Now Google says it's investigating the possibility of detecting diabetes and non-diabetes diseases using a smartphone camera, with the help of machine learning.
"Given the early promising results, we're looking forward to clinical research with partners, including EyePACS and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CGMH), to investigate if photos from smartphone cameras can help detect diabetes and non-diabetes diseases from external eye photos as well," wrote Greg Corrado, Head of Health AI at Google in a blog post.
Google's other research explores how a phone's built-in microphone could be used to record heart sounds. Listening to heart and lung sounds is a critical part of a physical exam, and usually, it's done using a stethoscope at clinics. However, Google envisions a future where anyone can record their heart sounds by simply placing their phone over the chest.
"Our latest research investigates whether a smartphone can detect heartbeats and murmurs. We're currently in the early stages of clinical study testing, but we hope that our work can empower people to use the smartphone as an additional tool for accessible health evaluation."
It's worth noting that the Google Fit app already allows you to measure your pulse and breath using your smartphone. It uses your phone's camera sensor and machine learning to track your heart and respiratory rates. The feature was initially exclusive to the Pixel phones, but Google says it's now available "on more than 100 models of Android devices, as well as iOS devices."
Source: Google Blog